The severity of the viral infection depends on many factors. Virulence of antigens, the collapse of the immune system, and the production of antibodies are factors. Delay in the production of antibodies due to prolonged antigenic phase can lead to complications. The antibodies are specific to different antigens and bind to particular receptors. Therefore, the antibodies are produced in various stages of infection.
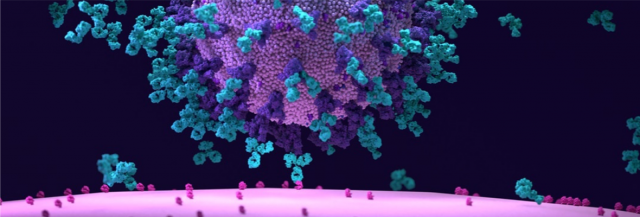
The SARS-CoV-2 virus begins infection as a typical Respiratory disease. As the antigen level drops, antibodies like IgM and IgA take place in the system. The IgM remains in the host system from the eighth day to the twenty-sixth day, along with IgA. After which, it disappears from the system. The secondary antibody in IgG remains in the system for the later part of the convalescent phase until the patient has recovered. Cell-mediated immunity plays a vital role in developing the defense mechanism of the host. After infection with SARS-CoV-2, individuals develop Neutralizing antibodies. The concentrations of these antibodies vary from one individual to the other depending on their immune response. Vaccination against COVID can boost the production of NAbs in the host.
The diagnosis of COVID depends on the detection of antibodies, thereby determining the stage of infection. The Diagnostic kits can screen both asymptomatic and symptomatic individuals. The novel pathogenicity SARS-CoV-2 posed many challenges for the development of antibody detection kits. The window period, the receptors, the antigenic proteins were all unknown for COVID. Hence, previous models of MERS and SARS helped in making the ideal cocktail of the antibodies. In addition, the analysis of local samples obtained in the course of the infection has helped to understand the use of specific antibodies.
Since the pandemic’s start, J Mitra & Co. is catering to the need for Antibody testing for COVID-19 infection. It became the first company to develop and manufacture the COVID-19 (IgM+IgA+IgG) ELISA kit, followed by the COVID-19 Kawach IgG ELISA kit. Both these kits suited well for the early and the late stages of the infection. The second wave of COVID-19 has proved to be more challenging. The use of Neutralizing Antibodies for the diagnosis of COVID addressed this challenge. The company developed the COVID-19 Neutralizing Antibody kit. It has >95% Sensitivity and 100% Specificity.